This post is about how to use Splunk logging driver in Docker. We will explain how to setup splunk server on a local environment and how can we feed splunk in with container(s) logs.
After you completed this post, you will be able to understand basic concept of docker logging driver and how to use it.
Docker logging drivers
Docker includes multiple logging mechanisms to help you get information from running containers and services. These mechanisms are called logging drivers.
Each Docker daemon has a default logging driver that each container uses it unless you configure to use a different logging driver.
| Driver | Description |
|---|---|
none |
No logs will be available for the container and docker logs will not return any output. |
json-file |
The logs are formatted as JSON. The default logging driver for Docker. |
syslog |
Writes logging messages to the syslog facility. The syslog daemon must be running on the host machine. |
journald |
Writes log messages to journald. The journald daemon must be running on the host machine. |
gelf |
Writes log messages to a Graylog Extended Log Format (GELF) endpoint such as Graylog or Logstash. |
fluentd |
Writes log messages to fluentd (forward input). The fluentd daemon must be running on the host machine. |
awslogs |
Writes log messages to Amazon CloudWatch Logs. |
splunk |
Writes log messages to splunk using the HTTP Event Collector. |
etwlogs |
Writes log messages as Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) events. Only available on Windows platforms. |
gcplogs |
Writes log messages to Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Logging. |
In this post we will explains splunk logging driver.
Splunk
In terms, Splunk that means as the below;
Splunk makes it simple to collect, analyze and act upon the untapped value of the big data generated by your technology infrastructure, security systems and business applications—giving you the insights to drive operational performance and business results.
Splunk logging driver
The splunk logging driver sends container logs to HTTP Event Collector in Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud. You can use splunk as default logging driver for Docker or set the logging driver for a specific container by using the –log-driver option to docker-run command.
You should configure deamon.json configuration file for use the splunk as the global logging driver. You should be add the following syntax to deamon.json and restart docker;
{
"log-driver": "splunk"
}
In this post we will use the container specific logging. Let’s begin.
Setup Splunk Server
We will setup splunk with basic definitions on local environment.
- Pull the splunk image from docker hub as follow;
docker pull splunk/splunk - Check the splunk image as follow;
➜ ~ docker images | grep splunk splunk/splunk latest 1b6fa73035a6 5 days ago 736MB - Start the splunk server as following command;
docker run -d -e "SPLUNK_START_ARGS=--accept-license" -e "SPLUNK_USER=root" -p "8000:8000" splunk/splunk - Go to localhost:8000 and see that splunk server is up.
- And then go to Settings -> Data inputs -> HTTP Event Collector -> Add new.
Step - 1
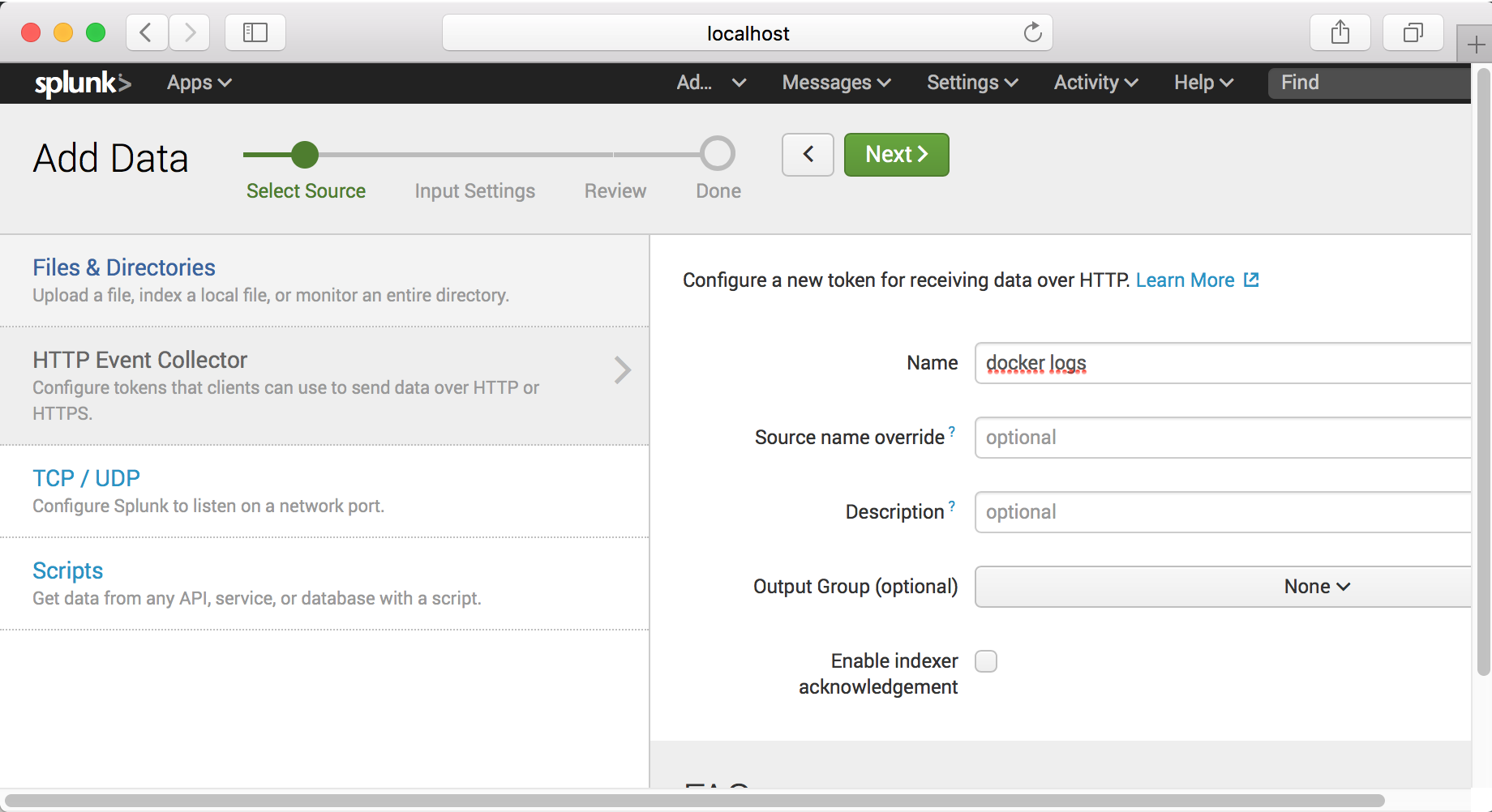
Step - 2
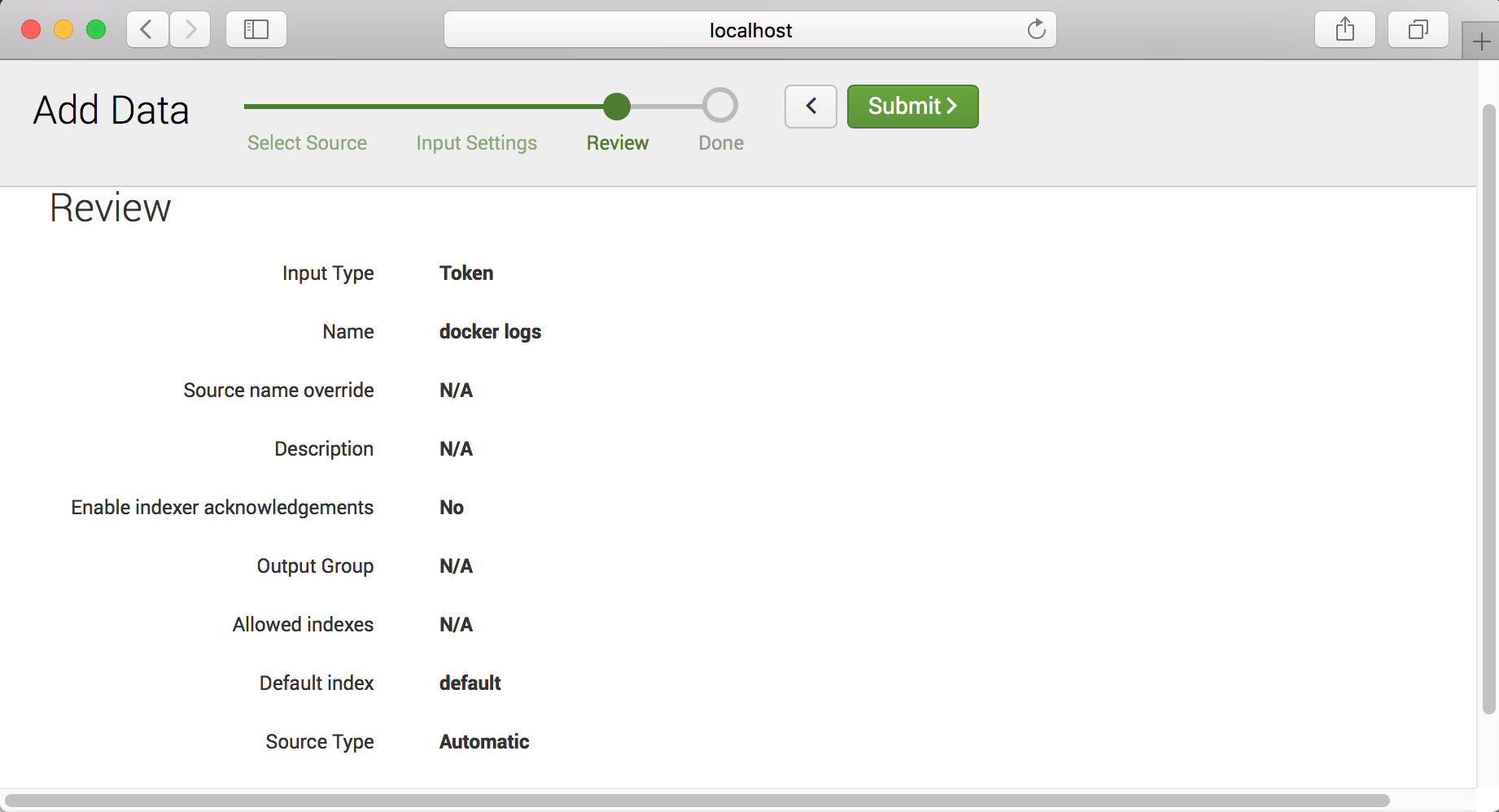
Step - 3
Note : You can copy token value in this step.
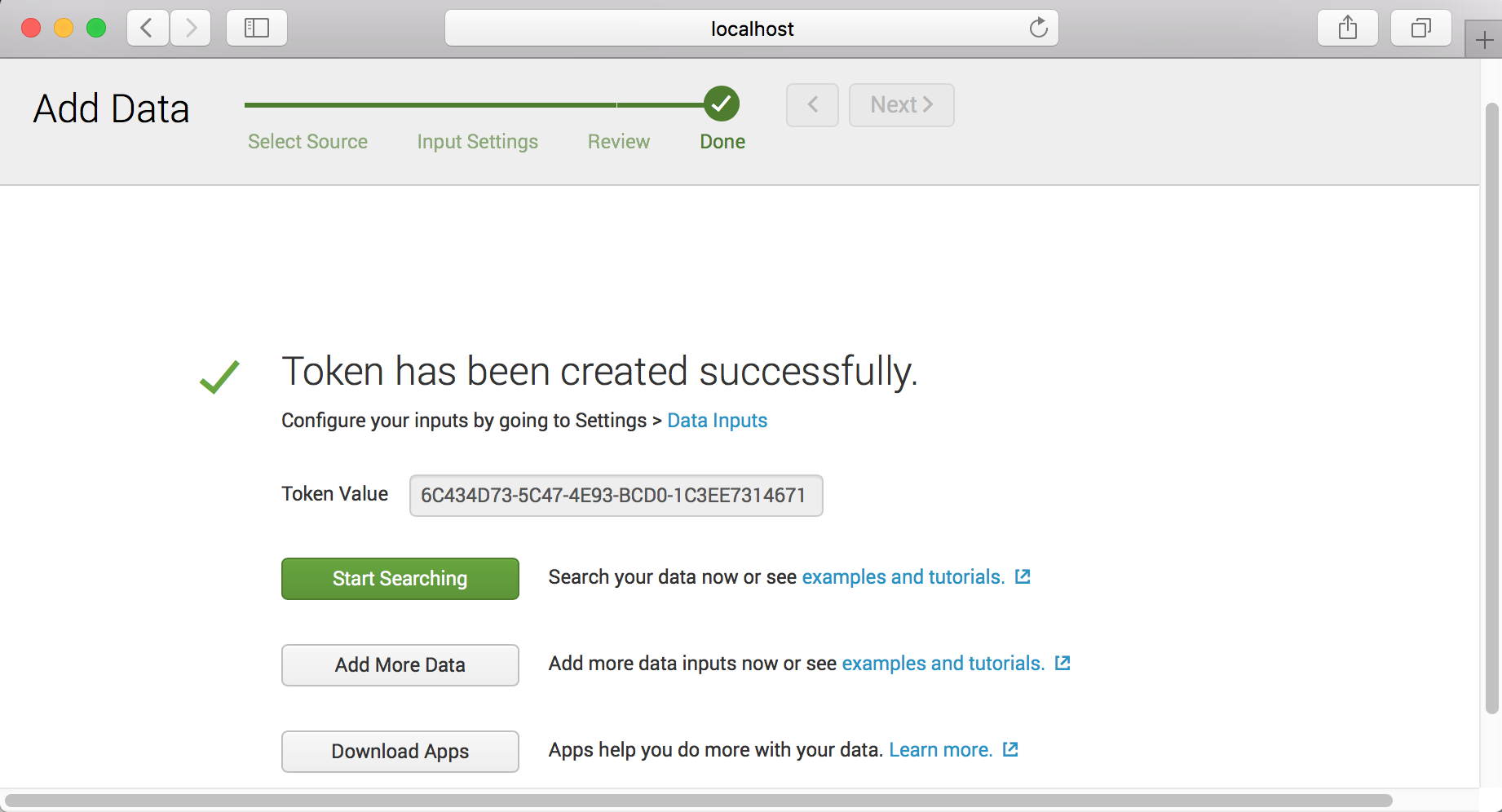
Step - 4
Note : If status of collector is disabled you can enable on the Global Settings
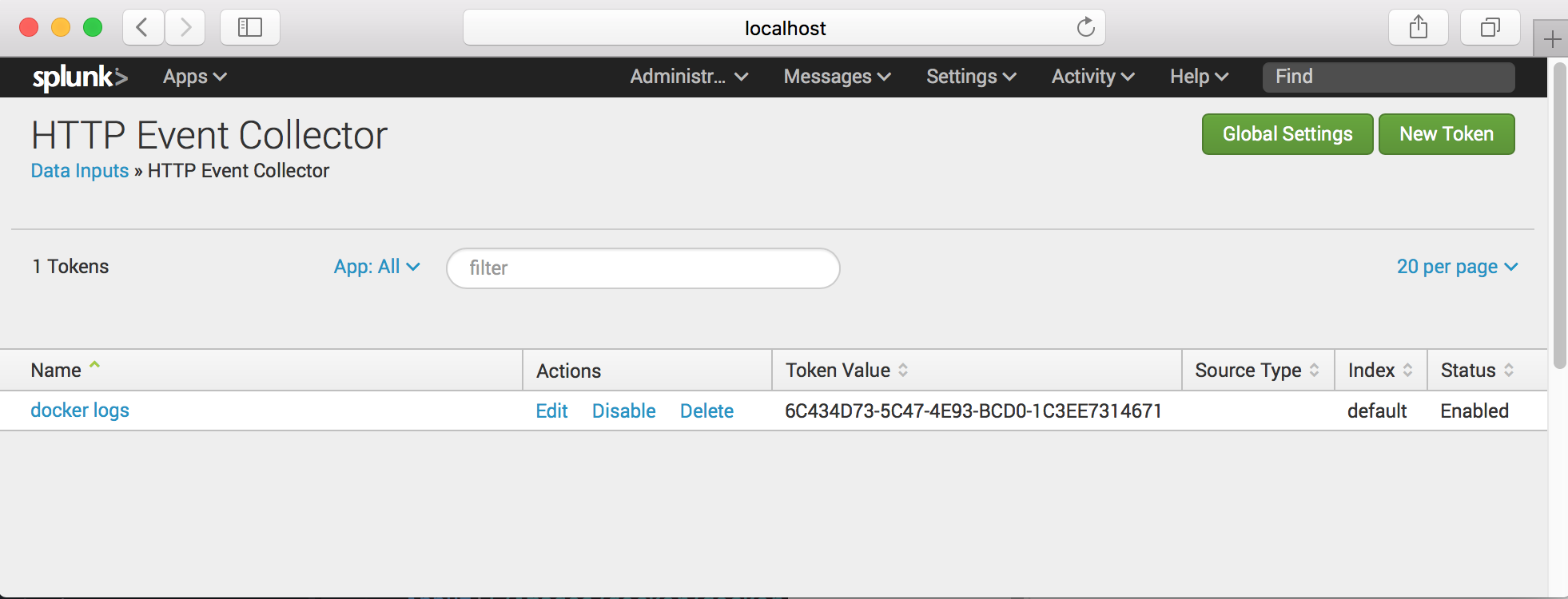
Step - 4
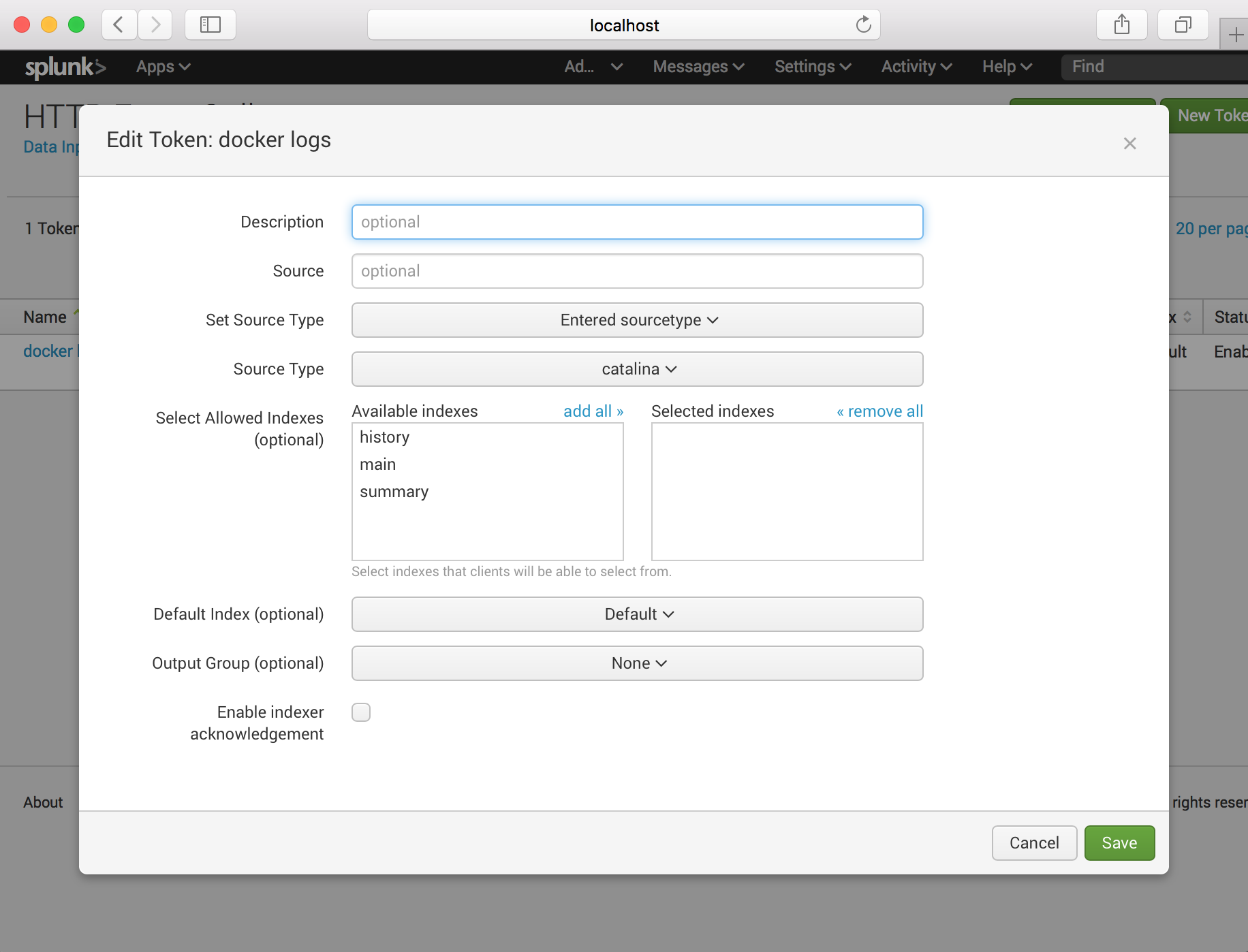
Click the “docker logs” and setup source type.
Note : We will use the nginx container logs with splunk. Therefore source type should be catalina.
We’ve completed splunk phase now. Let’s start the container with logging driver.
Setup Container with Splunk logging Driver
For see logs from container in splunk server, we will use the nginx container. We will run nginx with extra option for splunk.
Firstly we neet to know ip adress of splunk server. Please following command for this;
docker inspect -f '{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}' container_name_or_id
Above command output should look like this : 172.17.0.2
We ready for start nginx now;
docker run -p 80:80 --log-driver=splunk --log-opt splunk-url=http://172.17.0.2:8088 --log-opt splunk-token=6C434D73-5C47-4E93-BCD0-1C3EE7314671 --log-opt splunk-insecureskipverify=true nginx
We’ve some options for splunk. We will detailed in here;
- log-driver : Definitions of logging driver.
- splunk-url : Definitions of splunk http event collector url.
- splunk-token : Token for splunk http event collector.
- splunk-insecureskipverify : Instructs the driver to skip cert validation.
And see which containers running on docker;
➜ ~ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
64702bff9344 nginx "nginx -g 'daemon ..." 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp cocky_ritchie
257110abc652 splunk/splunk "/sbin/entrypoint...." 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 1514/tcp, 8088-8089/tcp, 8191/tcp, 9997/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8000->8000/tcp blissful_kalam
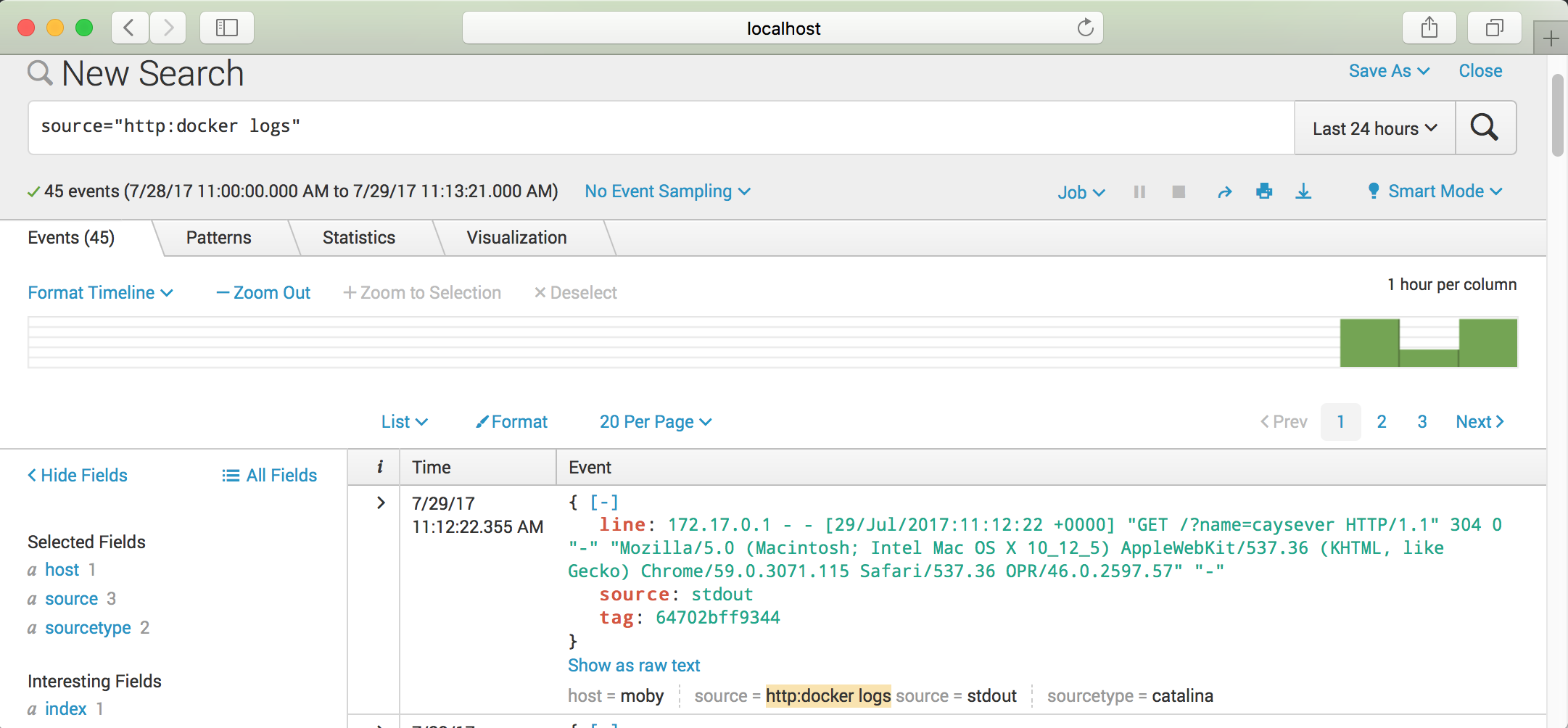
Now that the container is running, I can send some GET requests nginx to generate some logs output.
curl localhost:80
curl localhost:80?name=caysever
And we will see container logs on the splunk server;
Select the docker logs ;
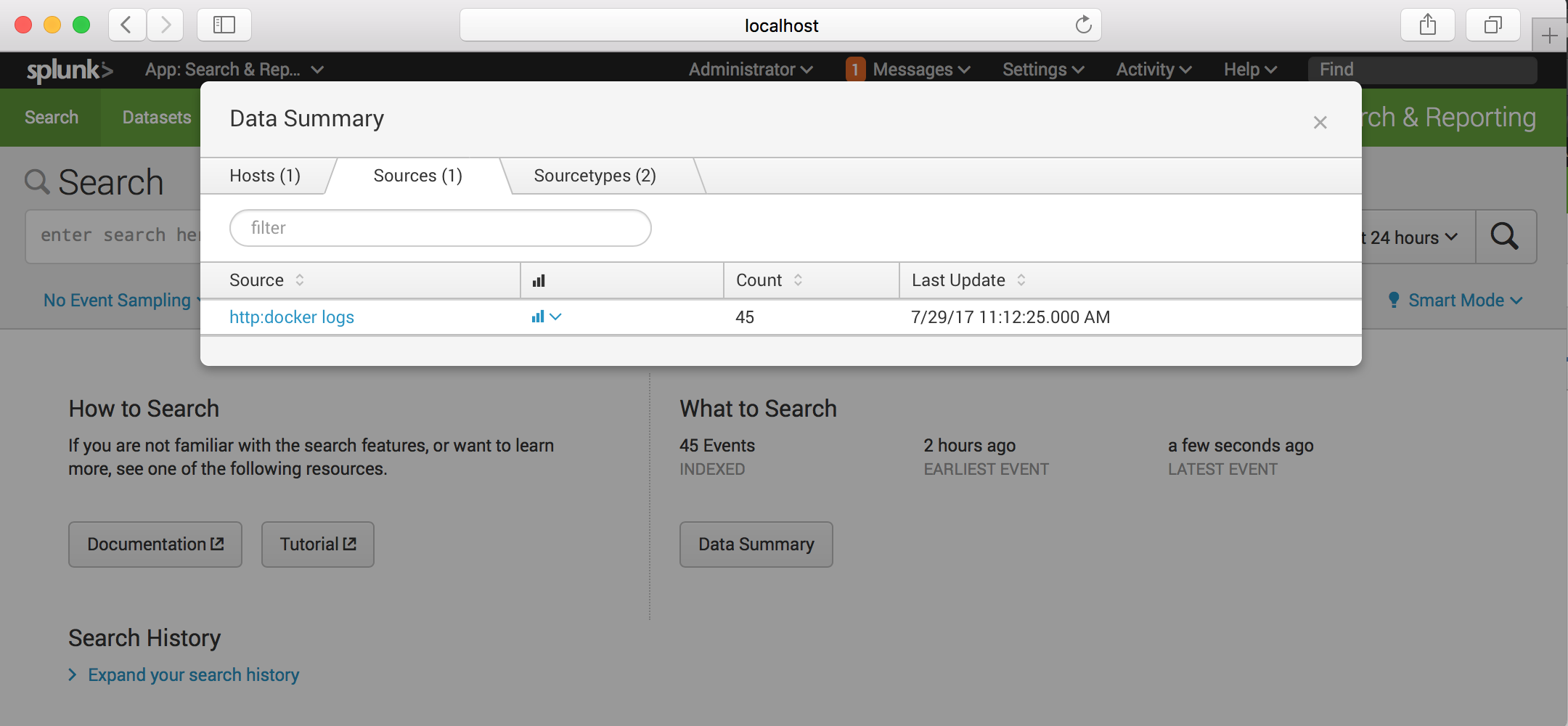
And see;
I hope this post is useful for you. See you at next posts.
comments powered by DisqusAlican Akkus.
